SOA OS23 is a modern approach to building IT systems using service-oriented architecture (SOA). It brings together modular services, cloud computing, APIs, and security-first design. The goal is to create systems that are scalable, secure, and easy to update.
This guide explains SOA OS23 in clear and simple language. It covers its features, layers, benefits, challenges, and use cases.
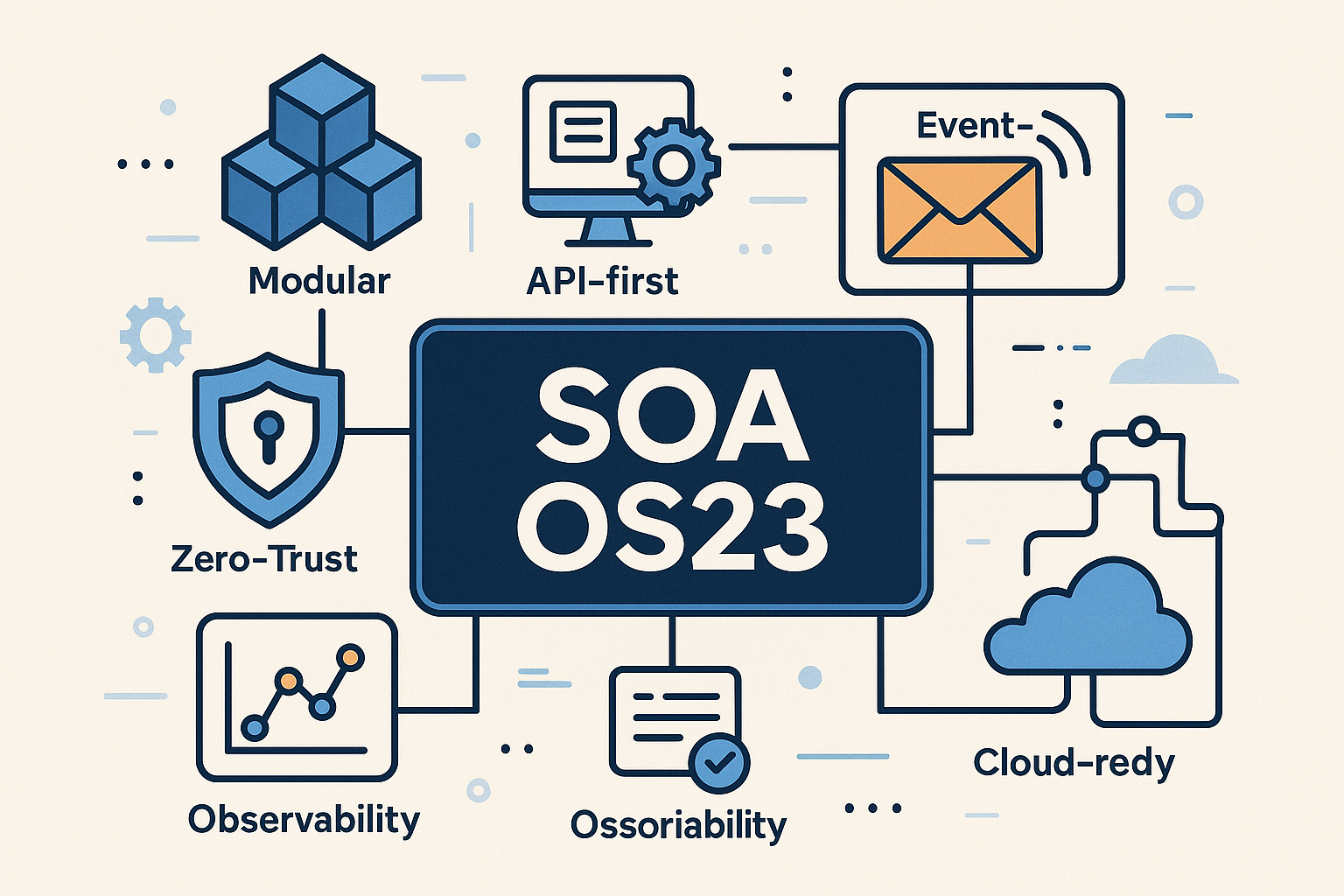
What Is SOA OS23?
SOA OS23 is a framework for digital systems. Instead of one large system, it uses many small parts called services. Each service has a specific job and can work independently. Services communicate through APIs or events.
This makes IT systems easier to scale, safer to run, and faster to update.
Key Features of SOA OS23
-
Modular structure – systems are divided into small services.
-
API-first – every service has a clear communication interface.
-
Event-driven design – services send and receive messages in real time.
-
Zero-trust security – every action is verified and protected.
-
Cloud-ready – works across hybrid and multi-cloud setups.
-
Observability – easy to monitor and troubleshoot.
SOA OS23 Architecture Layers
| Layer | Components |
|---|---|
| Integration | API gateways, service mesh, load balancers |
| Communication | Event brokers, message queues, streaming platforms |
| Security | Identity and access management, encryption, policy enforcement |
| Data | Databases, caches, real-time pipelines |
| Observability | Centralized logs, metrics dashboards, trace systems |
| Deployment | Kubernetes, containers, Infrastructure-as-Code (Terraform, Helm) |
Benefits of SOA OS23
-
Scalability – handle more users by adding services.
-
Resilience – one service failure does not break the whole system.
-
Faster delivery – services can be updated independently.
-
Compliance – easier to meet security and legal rules.
-
Future-ready – integrates with AI, IoT, and edge computing.
“With SOA OS23, organizations gain faster delivery and better system insights. Using tools such as Gramhir Pro can further enhance analytics and performance tracking.”
Challenges of SOA OS23
-
Complexity – needs careful design and planning.
-
Cost – cloud services can become expensive.
-
Skill gap – requires DevOps and security expertise.
-
Governance – without rules, services may grow in a messy way.
Use Cases of SOA OS23
| Industry | SOA OS23 Applications |
|---|---|
| Finance | Real-time fraud detection, online payments, digital banking |
| Healthcare | Patient data exchange, IoT medical devices, secure portals |
| Retail | Personalized shopping, live stock updates, mobile apps |
| Logistics | Tracking goods, warehouse automation, edge computing |
| Telecom | Billing systems, customer portals, network monitoring |
Adoption Roadmap
-
Assessment – review existing systems.
-
Pilot projects – start small with APIs and one or two services.
-
Service mesh rollout – add more services and connect them.
-
Governance – set rules for API versions and security.
-
Scaling – expand across the organization.
Governance and Best Practices
To succeed with SOA OS23, organizations need rules and processes:
-
API lifecycle management – track and update APIs.
-
Security audits – check for risks regularly.
-
Incident management – plan for service failures.
-
Observability reviews – analyze logs and metrics.
-
Training programs – prepare staff for cloud-native tools.
Future of SOA OS23
The future of SOA OS23 is strong. Trends include:
-
AI-driven automation for faster decision-making.
-
Serverless computing to reduce costs.
-
Edge computing for real-time data at local sites.
-
Global compliance standards to support data security.
Conclusion
SOA OS23 is a modern framework for building IT systems. It uses small, independent services, strong security, and cloud-native tools. Companies in finance, healthcare, retail, logistics, and telecom can all benefit from it.
With proper planning, governance, and training, SOA OS23 helps organizations create systems that are scalable, secure, and ready for the future.